
- October 16, 2025
- Maneesh Gupta
- 1
A Practical Guide for Network Engineers (Part 2: Advanced Strategies and Implementation)
What we learned after deploying link-state protocols and how you can apply it tomorrow
Before diving into the advanced strategies in Part II, make sure to check out Part I: Understanding the Basics. It lays the groundwork for everything we explore here. Read it now by clicking the link: “Link-State Protocols in Networking Without the Complexity”
Still Relying on RIP or IGRP? It’s Time to Move Forward
Many network engineers start their journey with RIP or IGRP which are reliable for small networks, but as traffic scales, their limits quickly show.
Long convergence times, inefficient bandwidth use, and routing loops begin to hurt performance.
Why? Because these distance-vector protocols know only their immediate neighbors. As networks grow, routers lose global visibility, and recovery from failures slows dramatically.
Why Traditional Routing Fail Today?
Older protocols update their routing tables periodically, taking precious seconds (or minutes) to react to change.
This local view of the network makes it impossible to calculate efficient paths in real time.
In high-scale environments, this means:
- Slow recovery during link failures
- High router resource consumption.
- Poor scalability as routing tables balloon
The Link-State Advantage
Modern enterprises solve these challenges with OSPF and IS-IS — protocols that give routers a complete map of the network.
Every router maintains its own copy of the network topology and uses Dijkstra’s Shortest Path Tree (SPT) algorithm to compute optimal routes.
The result? Faster convergence, smarter routing, and far better use of bandwidth.
Step 1: Define
Link-state protocols distribute information about each router’s links to all others in the domain.
Each node therefore has a global view of the topology which is essential for scalable and predictable routing decisions.
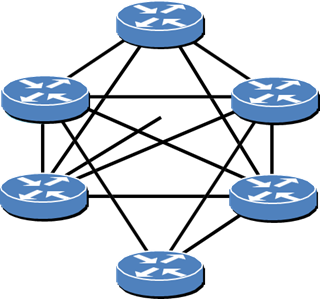
Step 2: Diagnose
Traditional protocols collapse under the weight of large networks because they lack this awareness.
Link-state protocols fix that by flooding LSAs (Link-State Advertisements) across the entire area, ensuring every router reacts instantly to topology change.
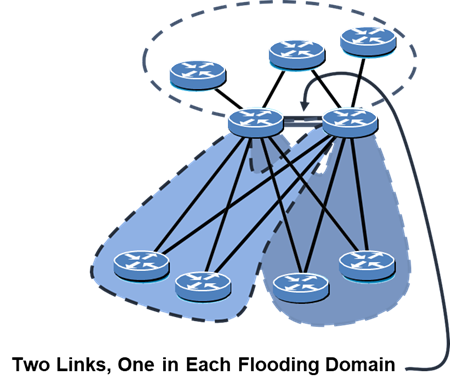
Step 3: Decide
In OSPF, Dijkstra’s algorithm continuously calculates the best routes.
In IS-IS, running directly over Layer 2, scalability improves even further — ideal for large-scale service-provider or campus environments.
Step 4: Deliver
When implemented correctly, link-state protocols provide:
- Near-real-time convergence after link or node failure.
- Efficient resource utilization.
- Reduced network downtime
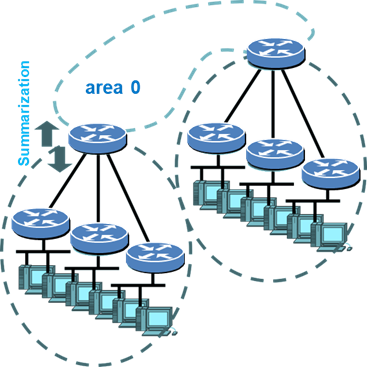
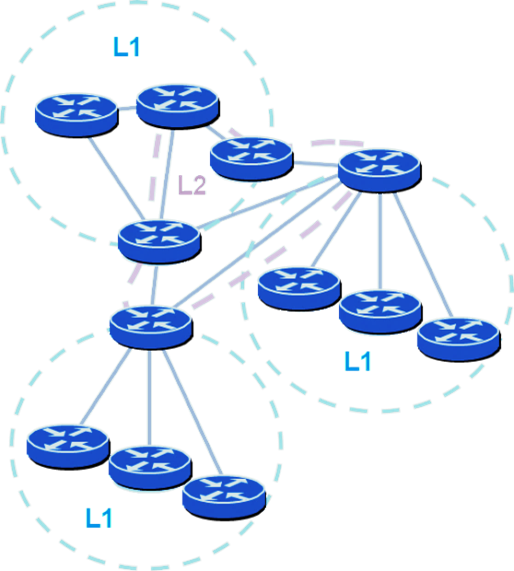
Case Study: Scaling a Global Network
A multinational organization operating across hundreds of offices struggled with slow recovery and unpredictable outages using RIP.
Actions Taken:
- Adopted OSPF for internal routing and IS-IS for the core.
- Segmented the network into multiple areas to reduce update overhead.
- Introduced real-time monitoring with SolarWinds and Wireshark.
- Conducted staff training on advanced configuration and optimization.
Results:
- 40 % faster convergence after failures
- Reduced downtime, boosting productivity company-wide
- 30 % smaller routing tables, lowering router CPU and memory use
What Did Not Work?
Initial misconfigurations in adjacency and area boundaries led to short routing loops — quickly fixed through retraining and configuration review.
The Advanced Link-State Playbook
Map Your Topology: Identify potential area boundaries and aggregation points.
Deploy in Phases: Start small, validate stability, then scale up.
Monitor Continuously: Track adjacency states and LSAs in real time.
Iterate and Optimize: Fine-tune area design, hello/dead timers, and SPF intervals.
💡 Start small — configure one router with OSPF or IS-IS, verify adjacencies, and analyze the SPT.
Key Takeaways
By moving to link-state routing, you unlock:
- Rapid convergence
- Intelligent, topology-aware routing decisions
- Efficient resource utilization across large networks.
The path forward is simple: expand deployment gradually, validate continuously, and keep configurations optimized as your network evolves.
At TelenceSolutions
We continue to help professionals build scalable, intelligent networks through real-world, hands-on learning — from OSPF and IS-IS fundamentals to BGP, SD-WAN, and AI-driven automation.
Stay tuned for the next post in this series — “From Link-State to BGP: Designing Networks for the Future.”


1 comment on “Advanced Link-State Routing Without the Complexity”