
- October 13, 2025
- Maneesh Gupta
- 0
What We Learned from Scaling Large Networks and How You Can Apply It?
As organizations expand, their networks face exponential traffic growth, evolving security threats, and complex multi-site connectivity requirements. Traditional routing methods like OSPF, ISIS, and MPLS often reach their limits creating bottlenecks, instability, and high maintenance overhead.
Why Traditional Approaches Fall Short?
Most enterprise networks today still:
- Depend heavily on IGPs such as OSPF or ISIS for internal routing.
- Utilize MPLS for scalability and VPNs, but struggle with its increasing complexity.
- Apply ACLs and PBR for traffic control, which become cumbersome at large scale.
The result?
- Limited scalability
- Frequent routing instability
- Complex, error-prone configuration management.
The BGP Advantage: A Smarter Framework for Modern Networks
At Eduinx, we implemented BGP as the primary routing protocol to overcome these challenges — and the results were transformative.
Step 1: Define the Network Needs
We started by identifying the key goals: scalability, traffic control, and security.
Solution: Implemented BGP with IPv4/v6 dual stack, enabling dynamic routing and granular traffic management.
Step 2: Diagnose Bottlenecks
Traditional IGP and MPLS architectures showed inefficiencies in bandwidth use and route propagation.
Solution: Introduced BGP Route Reflectors, Multicast VPN, and Label Unicast — making the network more dynamic and resilient.
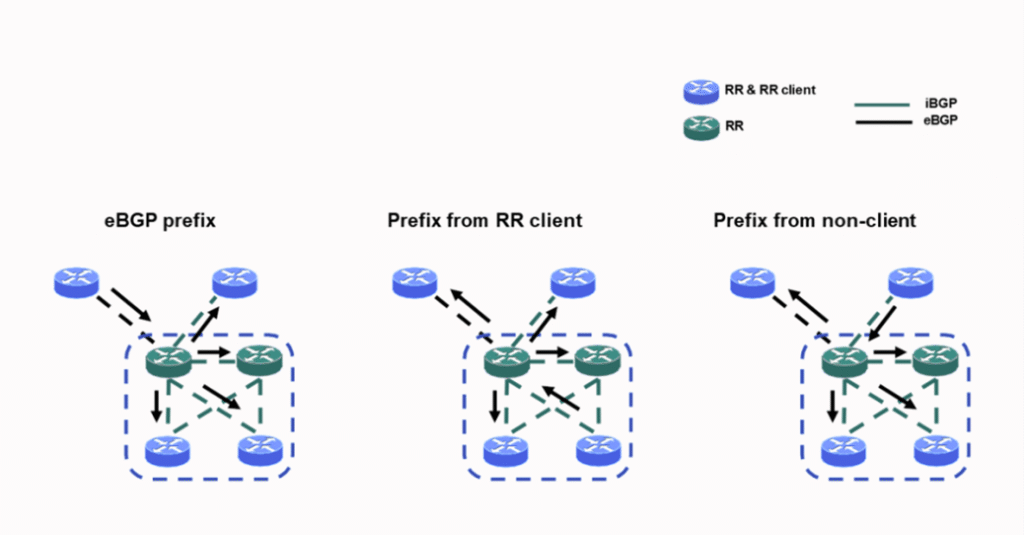
Step 3: Optimize Path Selection
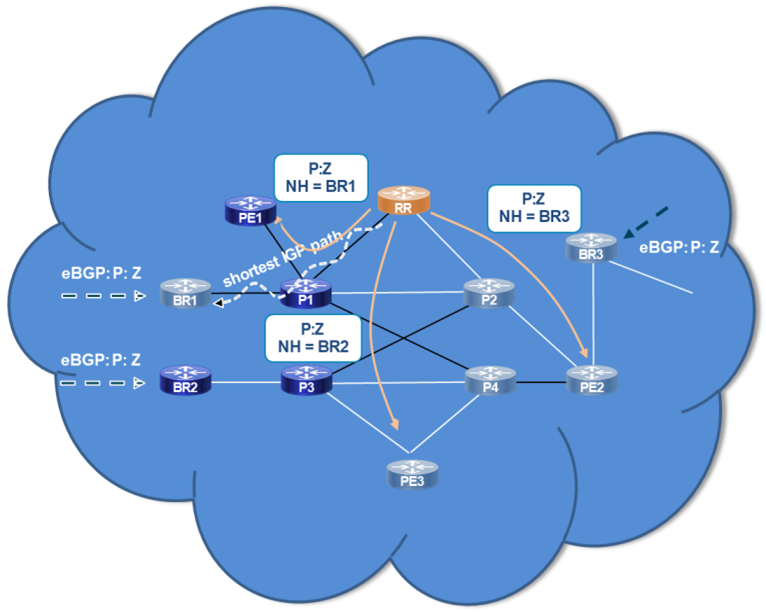
We leveraged BGP Path Selection Algorithms, fine-tuning attributes such as LOCAL_PREF, MED, and AS_PATH to ensure the best route selection across multiple exit points and peers.
Step 4: Deliver Intelligent BGP Policies
Using prefix-lists, route-maps, and BGP FlowSpec, we built adaptive routing policies that managed inbound/outbound traffic efficiently and mitigated DDoS attacks in real time.
Case Study: Scaling a Multi-Site Enterprise Network
A multi-site enterprise faced scalability challenges with its existing MPLS and IGP setup. Here’s what changed when we switched to BGP:
Actions Taken:
- Implemented BGP peering across multiple sites with IPv4/v6 and L3VPN support.
- Integrated BGP FlowSpec for advanced DDoS mitigation.
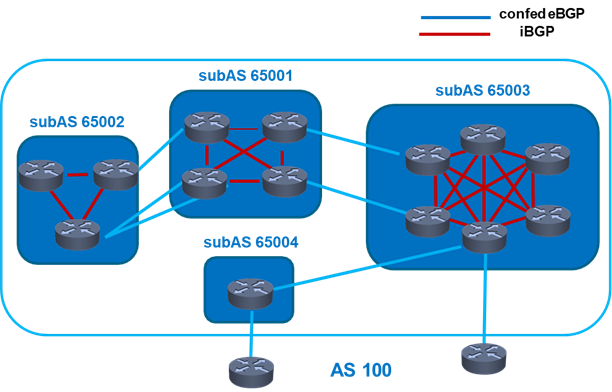
- Simplified the iBGP mesh using Route Reflectors and Confederations.
- 30% improvement in routing efficiency
- 25% reduction in management overhead
- 99.99% uptime over six months with zero major outages
The BGP Playbook for Network Engineers
Define Your Network Needs: Identify requirements for L3VPN, Multicast VPN, or SDN integration.
Diagnose Bottlenecks: Use BGP UPDATEs and SNMP to analyze routing inefficiencies.
Optimize Path Selection: Tune AS_PATH, LOCAL_PREF, and MED for better performance.
Implement Policies: Deploy prefix-lists, route-maps, and FlowSpec for dynamic traffic management.
Pro Tip: Always validate configurations in a test lab environment before production rollout.
Key Takeaways
BGP isn’t just for ISPs — it’s a strategic enabler for enterprise-grade scalability and resilience.
When configured correctly, it reduces downtime, enhances control, and prepares your network for future growth.
Next Step:
Start experimenting with BGP in your test network. Enable FlowSpec for security, use Route Reflectors for efficiency, and fine-tune your path selection algorithms for peak performance.
At TelenceSolutions
We continue to help professionals and enterprises master real-world networking skills that make a measurable impact — from BGP scaling to AI-driven network automation.
If you’re a network engineer, architect, or tech leader aiming to build high-performance, future-ready networks — this is your roadmap.

